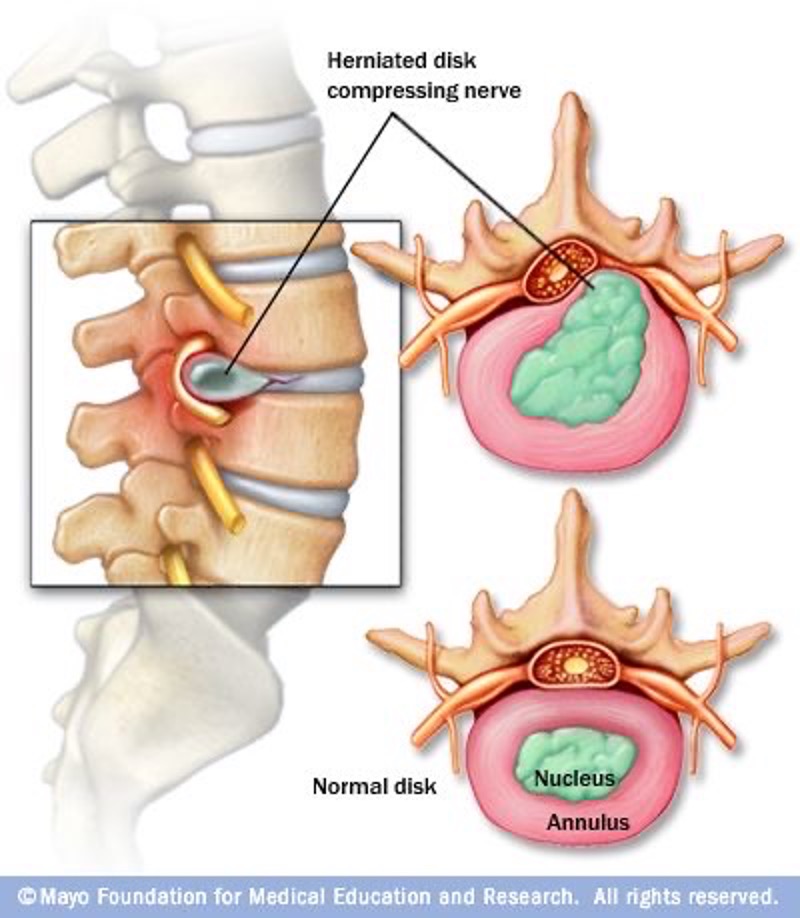
A spinal disc is made of an outer thick material and an inner softer substance. The two serve to cushion the vertebrae. A herniated disc occurs when there is a crack in the thick material allowing the softer substance to come out and rub against the nerve. This can happen anywhere along the spine. When it happens in the lower back, it is called lumbar herniated disc.
SYMPTOMS OF LUMBAR HERNIATED DISC
A herniated disc of the lumbar spine does not always cause symptoms. When it does, some of the symptoms include back pain, pain shooting from the back down the one leg or both legs. This is sometimes referred to as lumbar Radiculopathy or sciatica. Sometimes the affected leg can become weak. When foot is weak and you have trouble raising the foot, it is sometimes called a foot drop.
DIAGNOSIS OF LUMBAR HERNIATED DISC
To diagnose a lumbar herniated disc, your neurosurgeon usually performs a history and physical examination. If necessary, your neurosurgeon might order a diagnostic test such as a lumbar MRI, Lumbar CT scan or lumbar CT/Myelogram.
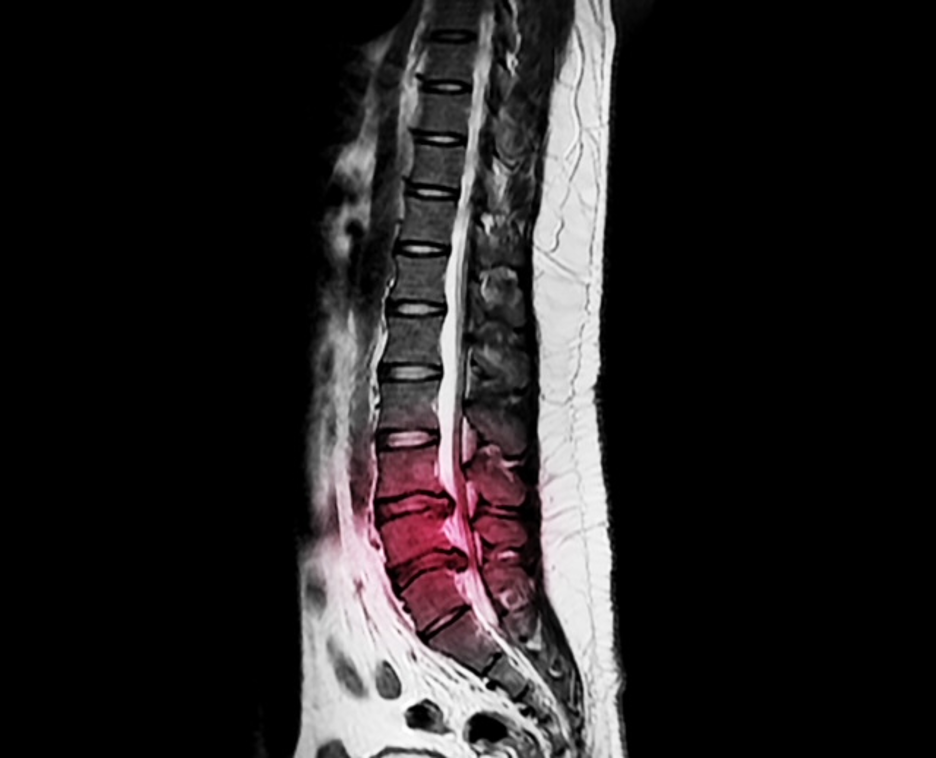
TREATMENT FOR LUMBAR HERNIATED DISC
Lumbar disc herniation may not require any treatment if there is no pain or loss of function or if the pain it is causing is mild. If treatment is required, it can be treat without surgery to see if the symptoms will improve. Sometimes your neurosurgeon may recommend surgery depending your individual case.
NON SURGICAL TREATMENT FOR LUMBAR HERNIATED DISC
Non surgical treatment for lumbar disc herniation includes medication to ease the discomfort, physical therapy or epidural steroid injections.
SURGICAL TREATMENT FOR LUMBAR HERNIATED DISC
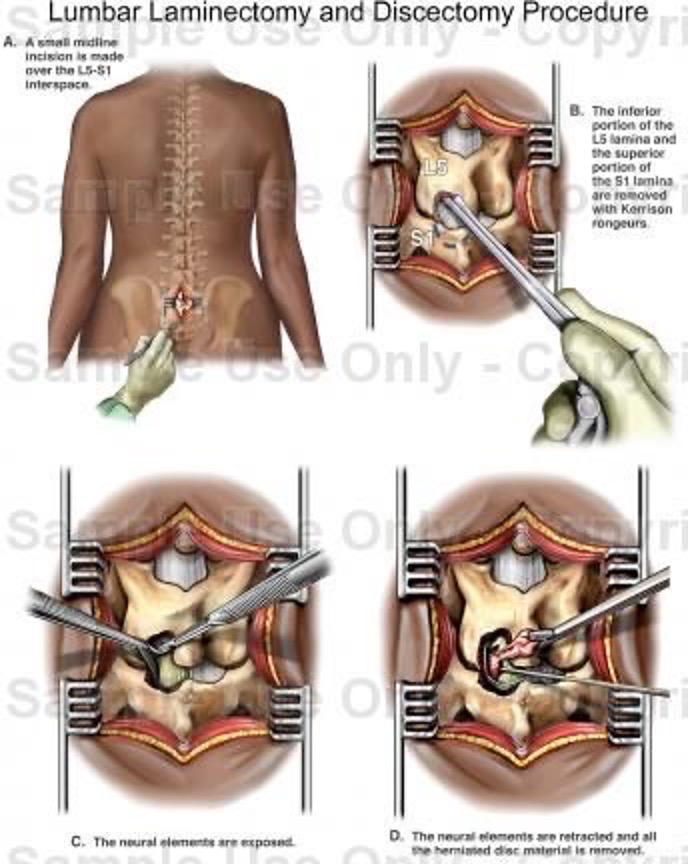
Surgery for Lumbar herniated disc usually involves performing a lumbar laminotomy with diskectomy or lumbar laminotomy with diskectomy. Whether lamintomy or laminectomy is performed depends on how much of a window through the bone needs to be created to remove the herniated disc. During the procedure your neurosurgeon usually removes the portion of the disc that is pressing on the nerve.