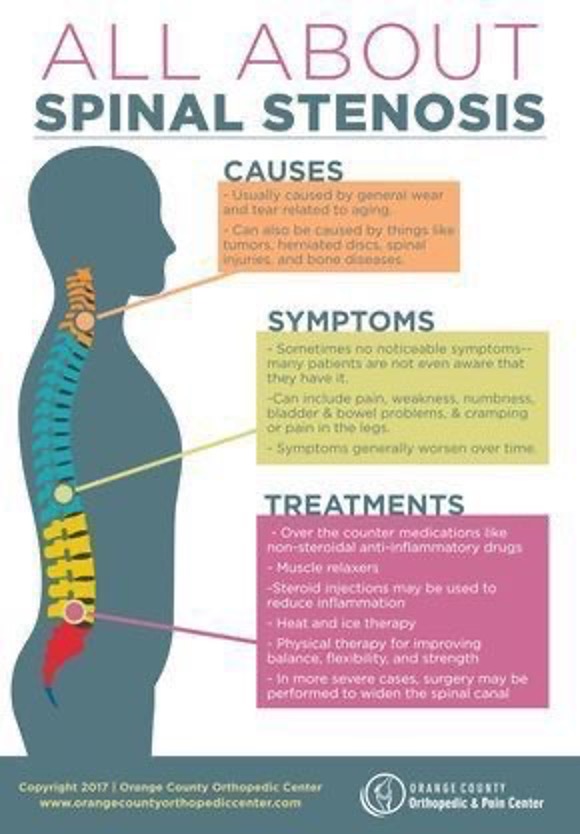
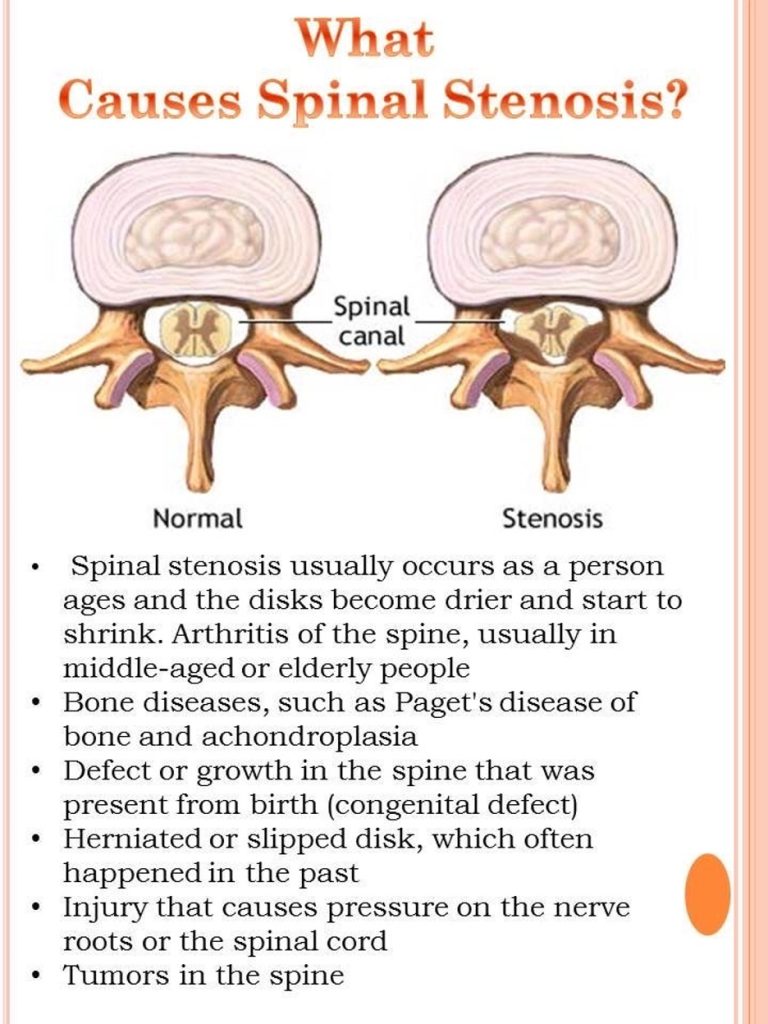
Spinal stenosis can occur anywhere along the spine. When it occurs in the thoracic segment of the spine, it is called thoracic spinal stenosis.
SYMPTOMS OF THORACIC SPINAL STENOSIS
The symptoms of thoracic spinal stenosis include mid back pain, pain shooting down the legs or along the rip cage which is often referred to as thoracic radiculopathy. Other symptoms include weakness in the legs, loss of balance which means the person might have thoracic myelopathy. Thoracic myelopathy is when the thoracic spinal stenosis is pinching on the spinal cord.
DIAGNOSIS OF THORACIC SPINAL STENOSIS
Your neurosurgeon usually performs a history and physical examination and orders the appropriate tests. Some of the tests used to diagnose thoracic spinal stenosis includes an MRI of the thoracic spine or CT/Myelogram of the thoracic spine.
TREATMENT OF THORACIC SPINAL STENOSIS
The treatment for thoracic spinal stenosis can be surgical or non surgical.
NON SURGICAL TREATMENT FOR THORACIC SPINAL STENOSIS
Non surgical treatment for thoracic spinal stenosis includes medications to ease the pain, physical therapy, epidural steroid injections.
SURGICAL TREATMENT FOR THORACIC SPINAL STENOSIS
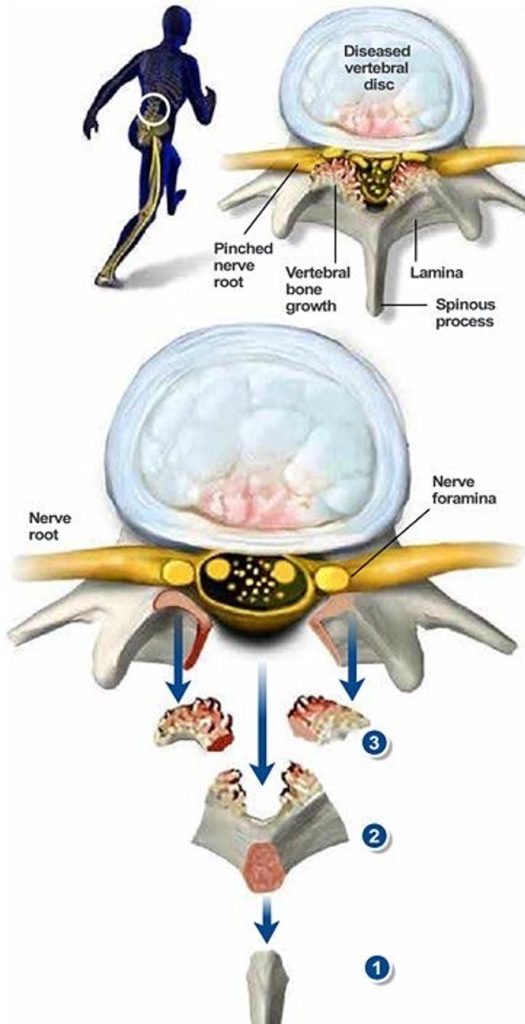
Surgical treatment for thoracic spinal stenosis is usually thoracic decompressive laminectomy. During the surgery your neurosurgeon removes the back part of the spine called the lamina, and creates more room for the nerves and the spinal cord. Sometimes your neurosurgeon may perform thoracic decompressive laminectomy with fusion. During this surgery your neurosurgeon removes the back part of the spine, creates more room for the nerves and spinal cord and also uses some screws and bone graft to fuse the vertebrae together if necessary.